Protobuf를 이용한 MCP 서버 구축 (2부) – Protoc 플러그인으로 MCP 서버 생성 자동화하기
Charlie Zhang
2025년 9월 21일
이 블로그 시리즈에서는 유용한 도구들로 가득 찬 MCP (Model Context Protocol) 서버를 구축하는 방법을 보여드립니다. 처음부터 시작하는 대신, 기존의 프로토콜 버퍼와 Google의 gRPC 트랜스코딩을 활용할 것입니다. 맞춤형 protoc (프로토콜 버퍼 컴파일러) 플러그인을 생성하여 MCP 서버를 자동으로 생성할 수 있습니다. 이 통합된 접근 방식을 통해 gRPC 서비스, OpenAPI 사양, REST API 및 MCP 서버를 모두 동일한 소스에서 생성할 수 있습니다.
이 블로그 시리즈는 4개의 기사로 구성되어 있습니다:
- 1부: gRPC 트랜스코딩을 사용하여 Protobuf에서 REST API 생성하기
- 2부: (본 기사) Protoc 플러그인으로 MCP 서버 생성 자동화하기
- 3부: Proto 주석으로 AI 상호작용 향상시키기
- 4부: 실제로 MCP 도구를 실행하면서 얻은 통찰력
구축할 내용
이 튜토리얼을 마치면 다음을 갖게 됩니다:
- proto 파일에서 MCP 서버를 생성하는 맞춤형 protoc 플러그인
- 어떤 메서드가 MCP 도구가 될지 표시하는 맞춤형 어노테이션
- 하나의 소스에서 gRPC, REST, MCP 코드를 생성하는 완전한 파이프라인
- AI 에이전트가 상호작용할 수 있는 작동하는 MCP 서버
이 기사에 언급된 모든 코드는 GitHub 저장소 **zhangcz828/proto-to-mcp-tutorial**에서 찾을 수 있습니다.
전제 조건
시작하기 전에, 1부를 완료했으며 다음을 갖추고 있는지 확인하세요:
- 1부의 서점 튜토리얼 프로젝트
- Go 1.19+ 설치
- Protocol Buffer 컴파일러 (protoc) 설치
- Python 3.8+ 설치 (MCP 서버 런타임용)
- npx 설치
프로토콜 버퍼 플러그인 생태계 이해하기
1부에서는 gRPC 트랜스코딩이 gRPC 및 REST API 정의를 통합하는 데 어떻게 도움이 되는지 보여드렸습니다. proto 파일에서 자동으로 생성된 깨끗하고 문서화가 잘 된 HTTP 엔드포인트를 갖게 되었죠. 하지만 곧 새로운 문제에 직면했습니다. Model Context Protocol을 통해 AI 시스템이 서비스와 상호작용하도록 만들고 싶었던 것입니다.
MCP는 AI 애플리케이션이 도구와 리소스에 프로그래밍 방식으로 접근하기 위한 표준화된 방법입니다. 우리의 통합된 접근 방식이 없었다면, 각 서비스에 대해 수동으로 MCP 서버 코드를 작성해야 했을 것입니다. 이는 기본적으로 gRPC 서비스, REST 엔드포인트 및 OpenAPI 사양과 함께 유지 관리해야 할 네 번째 API 정의 세트를 만드는 것과 같았습니다.
이때 우리는 protoc 기반 접근 방식을 확장할 수 있다는 것을 깨달았습니다. proto 파일에서 REST API와 OpenAPI 사양을 생성할 수 있다면, MCP 서버도 생성할 수 있지 않을까요? REST 엔드포인트 생성을 안내했던 동일한 HTTP 어노테이션이 MCP 도구를 구조화하는 방법을 알려줄 수 있었습니다.
프로젝트 설정
1부의 튜토리얼 프로젝트를 확장하는 것부터 시작하겠습니다. 튜토리얼 디렉토리로 돌아가 다음 명령을 실행하세요:
cd proto-to-mcp-tutorial
# 플러그인 및 MCP 코드용 디렉토리 생성
mkdir -p plugins/protoc-gen-mcp
mkdir -p generated/mcp
mkdir -p google/protobuf
mkdir -p mcp/protobuf
프로젝트 구조는 이제 MCP 관련 디렉토리가 추가되어 다음과 같아야 합니다:
proto-to-mcp-tutorial
├── cmd
│ └── server
│ └── main.go
├── generate.sh
├── generated
│ ├── go
│ │ ├── bookstore_grpc.pb.go
│ │ ├── bookstore.pb.go
│ │ └── bookstore.pb.gw.go
│ ├── mcp # New
│ └── openapi
│ └── openapi.yaml
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── google
│ └── protobuf # New
├── mcp # New
│ └── protobuf
├── googleapis
│ └── google
│ └── api
│ ├── annotations.proto
│ └── http.proto
├── plugins # New
│ └── protoc-gen-mcp
├── proto
│ └── bookstore.proto
└── README.md
맞춤형 MCP 어노테이션 생성
1. 필수 proto 파일 다운로드
curl -o google/protobuf/descriptor.proto \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/protocolbuffers/protobuf/refs/heads/main/src/google/protobuf/descriptor.proto
2. MCP 어노테이션 정의
어떤 RPC 메서드가 MCP 도구가 되어야 하는지 표시하기 위해 맞춤형 어노테이션을 생성해야 합니다. 새 파일 **mcp/protobuf/annotations.proto**를 생성합니다:
syntax = "proto3";
package example.v1;
option go_package = "proto-to-mcp-tutorial/generated/go/mcp;mcp";
import "google/protobuf/descriptor.proto";
// 메서드를 MCP 도구로 표시하기 위한 맞춤 확장 (50003은 사용자 지정 확장 필드 번호)
extend google.protobuf.MethodOptions {
MCPOptions mcp = 50003;
}
message MCPOptions {
// 이 메서드가 MCP 도구로 노출되어야 하는지 여부
bool enabled = 1;
}
3. MCP 어노테이션용 Go 코드 생성
export GOOGLEAPIS_DIR=./googleapis
export MCP_DIR=.
protoc -I${GOOGLEAPIS_DIR} -I${MCP_DIR} --go_out=./generated/go --go_opt=paths=source_relative mcp/protobuf/annotations.proto
MCP 어노테이션으로 Bookstore Proto 파일 업데이트
이제 proto/bookstore.proto 파일에 MCP 어노테이션을 추가하여 어떤 메서드를 MCP 도구로 활성화할지 표시합니다.
syntax = "proto3";
package bookstore.v1;
import "google/api/annotations.proto";
import "mcp/protobuf/annotations.proto";
option go_package = "generated/go/bookstore/v1";
service BookstoreService {
// Get a book by ID
rpc GetBook(GetBookRequest) returns (Book) {
option (google.api.http) = {
get: "/v1/books/{book_id}"
};
option (mcp.v1.tool) = {
enabled: true
};
}
// Create a new book
rpc CreateBook(CreateBookRequest) returns (Book) {
option (google.api.http) = {
post: "/v1/books"
body: "book"
};
option (mcp.v1.tool) = {
enabled: true
};
}
}
message Book {
string book_id = 1;
string title = 2;
string author = 3;
int32 pages = 4;
}
message GetBookRequest {
// The ID of the book to retrieve
string book_id = 1;
}
message CreateBookRequest {
// The book object to create
Book book = 1;
}
protoc-gen-mcp 플러그인 구축
plugins/protoc-gen-mcp/main.go 파일에 맞춤형 protoc 플러그인 코드를 작성합니다. 이 Go 플러그인은 proto 파일을 구문 분석하고, MCP 어노테이션을 확인한 다음, Python MCP 서버 코드를 생성합니다.
package main
import (
"bytes"
"fmt"
"regexp"
"strings"
"text/template"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/compiler/protogen"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/proto"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/reflect/protoreflect"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/types/descriptorpb"
"google.golang.org/protobuf/types/pluginpb"
mcpannotations "proto-to-mcp-tutorial/generated/go/mcp/protobuf"
httpannotations "google.golang.org/genproto/googleapis/api/annotations"
)
func main() {
protogen.Options{}.Run(func(gen *protogen.Plugin) error {
gen.SupportedFeatures = uint64(pluginpb.CodeGeneratorResponse_FEATURE_PROTO3_OPTIONAL)
// Extract MCP methods from the proto files
mcpMethods := extractMCPMethods(gen)
if len(mcpMethods) == 0 {
return nil // No MCP methods found
}
// Generate main server file
generateMCPServer(gen, mcpMethods)
return nil
})
}
type MCPMethod struct {
Service *protogen.Service
Method *protogen.Method
ToolName string
Description string
HTTPInfo *HTTPInfo
Input *protogen.Message
Output *protogen.Message
Parameters []*MCPParameter
}
type MCPParameter struct {
Name string
Type string
Required bool
Description string
}
type HTTPInfo struct {
Method string
Path string
Body string
}
func extractMCPMethods(gen *protogen.Plugin) []*MCPMethod {
var mcpMethods []*MCPMethod
for _, file := range gen.Files {
if !file.Generate {
continue
}
for _, service := range file.Services {
for _, method := range service.Methods {
if hasMCPToolAnnotation(method) {
mcpMethod := &MCPMethod{
Service: service,
Method: method,
ToolName: generateToolName(method),
Description: extractDescription(method),
HTTPInfo: extractHTTPInfo(method),
Input: method.Input,
Output: method.Output,
Parameters: extractParameters(method.Input),
}
mcpMethods = append(mcpMethods, mcpMethod)
}
}
}
}
return mcpMethods
}
func hasMCPToolAnnotation(method *protogen.Method) bool {
options := method.Desc.Options().(*descriptorpb.MethodOptions)
if options == nil {
return false
}
// Check if method has mcp.v1.tool annotation
if !proto.HasExtension(options, mcpannotations.E_Tool) {
return false
}
// Get annotation value and check if enabled
toolOptions := proto.GetExtension(options, mcpannotations.E_Tool).(*mcpannotations.MCPToolOptions)
return toolOptions != nil && toolOptions.Enabled
}
func extractParameters(inputType *protogen.Message) []*MCPParameter {
var parameters []*MCPParameter
if inputType != nil {
for _, field := range inputType.Fields {
param := &MCPParameter{
Name: string(field.Desc.Name()),
Type: getFieldType(field),
Required: isFieldRequired(field),
Description: extractFieldDescription(field),
}
parameters = append(parameters, param)
}
}
return parameters
}
func isFieldRequired(field *protogen.Field) bool {
// In proto3, technically all fields are optional, but for business logic:
// If the field not marked as optional keyword, consider it required
if field.Desc.HasOptionalKeyword() {
return false
}
return true
}
func getFieldType(field *protogen.Field) string {
// Check if the field is repeated (array/list)
if field.Desc.Cardinality() == protoreflect.Repeated {
return "list"
}
switch field.Desc.Kind() {
case protoreflect.StringKind:
return "string"
case protoreflect.Int32Kind, protoreflect.Int64Kind:
return "integer"
case protoreflect.BoolKind:
return "boolean"
case protoreflect.MessageKind:
return "object"
case protoreflect.EnumKind:
return "string"
default:
return "string"
}
}
func extractFieldDescription(field *protogen.Field) string {
if field.Comments.Leading != "" {
return strings.TrimSpace(string(field.Comments.Leading))
}
return ""
}
func generateToolName(method *protogen.Method) string {
methodName := string(method.Desc.Name())
// Convert to snake_case
methodName = camelToSnake(methodName)
return methodName
}
func camelToSnake(str string) string {
re := regexp.MustCompile("([a-z0-9])([A-Z])")
snake := re.ReplaceAllString(str, "${1}_${2}")
return strings.ToLower(snake)
}
func extractDescription(method *protogen.Method) string {
if method.Comments.Leading != "" {
return strings.TrimSpace(string(method.Comments.Leading))
}
return fmt.Sprintf("Execute %s RPC method", method.Desc.Name())
}
func extractHTTPInfo(method *protogen.Method) *HTTPInfo {
options := method.Desc.Options().(*descriptorpb.MethodOptions)
if options == nil {
return nil
}
if !proto.HasExtension(options, httpannotations.E_Http) {
return nil
}
httpRule := proto.GetExtension(options, httpannotations.E_Http).(*httpannotations.HttpRule)
if httpRule == nil {
return nil
}
info := &HTTPInfo{}
switch pattern := httpRule.Pattern.(type) {
case *httpannotations.HttpRule_Get:
info.Method = "GET"
info.Path = pattern.Get
case *httpannotations.HttpRule_Post:
info.Method = "POST"
info.Path = pattern.Post
info.Body = httpRule.Body
case *httpannotations.HttpRule_Put:
info.Method = "PUT"
info.Path = pattern.Put
info.Body = httpRule.Body
case *httpannotations.HttpRule_Delete:
info.Method = "DELETE"
info.Path = pattern.Delete
case *httpannotations.HttpRule_Patch:
info.Method = "PATCH"
info.Path = pattern.Patch
info.Body = httpRule.Body
}
return info
}
func generateMCPServer(gen *protogen.Plugin, mcpMethods []*MCPMethod) {
outputFile := gen.NewGeneratedFile("mcp_server.py", ".")
funcMap := template.FuncMap{
"contains": func(s, substr string) bool {
return strings.Contains(s, substr)
},
"printf": fmt.Sprintf,
"indent": func(text string, spaces int) string {
if text == "" {
return text
}
lines := strings.Split(text, "\n")
indentStr := strings.Repeat(" ", spaces)
var result []string
for i, line := range lines {
if strings.TrimSpace(line) != "" {
result = append(result, indentStr+line)
} else if i < len(lines)-1 { // Keep empty lines except the last one
result = append(result, "")
}
}
return strings.Join(result, "\n")
},
}
tmpl := template.Must(template.New("mcp_server").Funcs(funcMap).Parse(mcpServerTemplate))
var buf bytes.Buffer
if err := tmpl.Execute(&buf, mcpMethods); err != nil {
return
}
outputFile.P(buf.String())
}
const mcpServerTemplate = `#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
MCP Server for UPM API - Auto-generated from Protocol Buffers
This server provides access to project management operations
through the Model Context Protocol.
"""
import os
import sys
from typing import Any
import json
import httpx
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
API_BASE = 'http://localhost:8080'
VERIFY_SSL = False
# Initialize FastMCP
mcp = FastMCP('Bookstore Server')
async def make_api_request(url: str, method: str = "GET", payload: dict = None) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a HTTP request to the specified URL."""
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
}
# Use SSL verification based on environment variable
async with httpx.AsyncClient(verify=VERIFY_SSL) as client:
try:
if method.upper() == "GET":
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
elif method.upper() == "PUT":
response = await client.put(url, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=30.0)
elif method.upper() == "POST":
response = await client.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=30.0)
elif method.upper() == "DELETE":
response = await client.delete(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
elif method.upper() == "PATCH":
response = await client.patch(url, headers=headers, json=payload, timeout=30.0)
else:
return {"error": f"Unsupported HTTP method: {method}"}
response.raise_for_status()
# Handle DELETE responses that might be empty
if method.upper() == "DELETE":
if response.status_code == 200 or response.status_code == 204:
return {"success": True, "message": "Resource deleted successfully"}
# Try to parse JSON, return empty dict if no content
try:
return response.json()
except:
return {"success": True}
except httpx.HTTPStatusError as e:
return {"error": f"HTTP {e.response.status_code}: {e.response.text}"}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": str(e)}
# MCP Tools
{{range .}}
@mcp.tool()
async def {{.ToolName}}({{range $i, $param := .Parameters}}{{if $i}}, {{end}}{{$param.Name}}: {{if eq $param.Type "string"}}str{{else if eq $param.Type "integer"}}int{{else if eq $param.Type "boolean"}}bool{{else if eq $param.Type "list"}}list{{else}}dict{{end}}{{if not $param.Required}} = None{{end}}{{end}}) -> str:
"""{{.Description}}
{{if .HTTPInfo}}
HTTP: {{.HTTPInfo.Method}} {{.HTTPInfo.Path}}{{end}}
Parameters:{{range .Parameters}}
- {{.Name}} ({{.Type}}{{if not .Required}}, optional{{end}}): {{if contains .Description "\n"}}{{indent .Description 6}}{{else}}{{.Description}}{{end}}{{end}}
Returns:
- str: JSON formatted response from the API containing the result or error information
"""
try:
{{if .HTTPInfo}}
# Construct the URL
url = f"{API_BASE}{{.HTTPInfo.Path}}"
{{$httpInfo := .HTTPInfo}}{{range .Parameters}}{{if and .Required (contains $httpInfo.Path (printf "{%s}" .Name))}}
url = url.replace("{" + "{{.Name}}" + "}", str({{.Name}})){{end}}{{end}}
# Prepare payload for non-GET requests
payload = {}
{{range .Parameters}}{{if and (ne $httpInfo.Method "GET") (ne $httpInfo.Method "DELETE") (not (contains $httpInfo.Path (printf "{%s}" .Name)))}}
{{if .Required}}payload["{{.Name}}"] = {{.Name}}{{else}}if {{.Name}} is not None:
payload["{{.Name}}"] = {{.Name}}{{end}}{{end}}{{end}}
# Make the API request
result = await make_api_request(url, "{{.HTTPInfo.Method}}", payload if payload else None)
{{else}}
result = {"error": "No HTTP endpoint defined for this method"}{{end}}
# Return formatted JSON response
import json
return json.dumps(result, indent=2)
except Exception as e:
# Handle any errors that occur during execution
import json
error_result = {
"error": f"Tool execution failed: {str(e)}",
"tool_name": "{{.ToolName}}",
"error_type": type(e).__name__
}
return json.dumps(error_result, indent=2)
{{end}}
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Run the MCP server
mcp.run()
`플러그인 컴파일
# 프로젝트 루트 경로에서 실행
go build -o protoc-gen-mcp plugins/protoc-gen-mcp/main.go
모든 코드 생성하기
generate.sh 스크립트를 업데이트하여 MCP 서버 생성 단계를 포함합니다.
#!/bin/bash
export GOOGLEAPIS_DIR=./googleapis
export MCP_DIR=.
echo "Checking for required protoc plugins..."
# Check if protoc-gen-go is available
if ! command -v protoc-gen-go &> /dev/null; then
echo "❌ protoc-gen-go not found. Installing..."
go install google.golang.org/protobuf/cmd/protoc-gen-go@latest
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "⚠️ Failed to install protoc-gen-go. Skipping Go generation."
exit 1
fi
fi
# Check if protoc-gen-go-grpc is available
if ! command -v protoc-gen-go-grpc &> /dev/null; then
echo "❌ protoc-gen-go-grpc not found. Installing..."
go install google.golang.org/grpc/cmd/protoc-gen-go-grpc@latest
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "⚠️ Failed to install protoc-gen-go-grpc. Skipping gRPC generation."
exit 1
fi
fi
# Check if protoc-gen-grpc-gateway is available
if ! command -v protoc-gen-grpc-gateway &> /dev/null; then
echo "❌ protoc-gen-grpc-gateway not found. Installing..."
go install github.com/grpc-ecosystem/grpc-gateway/v2/protoc-gen-grpc-gateway@latest
if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "⚠️ Failed to install protoc-gen-grpc-gateway. Skipping Gateway generation."
exit 1
fi
fi
echo "🔧 Generating Go gRPC code..."
# Step 1: Generate Go code for MCP annotations
echo "🔧 Generating MCP annotations Go code..."
protoc -I${GOOGLEAPIS_DIR} -I${MCP_DIR} --go_out=./generated/go --go_opt=paths=source_relative mcp/protobuf/annotations.proto
# Step 2: Generate Go gRPC code
protoc -I${GOOGLEAPIS_DIR} -I${MCP_DIR} --proto_path=proto --go_out=./generated/go --go_opt paths=source_relative --go-grpc_out=./generated/go --go-grpc_opt paths=source_relative bookstore.proto
# Generate gRPC Gateway for REST endpoints
echo "🔧 Generating gRPC Gateway..."
protoc -I${GOOGLEAPIS_DIR} -I${MCP_DIR} --proto_path=proto --grpc-gateway_out=./generated/go --grpc-gateway_opt paths=source_relative bookstore.proto
# Generate OpenAPI specifications
echo "🔧 Generating OpenAPI spec..."
protoc -I${GOOGLEAPIS_DIR} -I${MCP_DIR} -I./proto --openapi_out=./generated/openapi \
--openapi_opt=fq_schema_naming=true \
--openapi_opt=version="1.0.0" \
--openapi_opt=title="Bookstore API" \
bookstore.proto
# Generate MCP server (always available since we have our custom plugin)
echo "🔧 Generating MCP server..."
protoc -I${GOOGLEAPIS_DIR} -I${MCP_DIR} --proto_path=proto \
--plugin=protoc-gen-mcp=./protoc-gen-mcp \
--mcp_out=./generated/mcp \
bookstore.proto
echo ""
echo "🎉 Generation complete!"
echo "📁 Check the ./generated directory for all generated files."업데이트된 생성 스크립트를 실행합니다:
./generate.sh
아래와 같은 결과 값을 볼수 있습니다:
Checking for required protoc plugins...
🔧 Generating Go gRPC code...
🔧 Generating MCP annotations Go code...
🔧 Generating gRPC Gateway...
🔧 Generating OpenAPI spec...
🔧 Generating MCP server...
🎉 Generation complete!
📁 Check the ./generated directory for all generated files.
생성된 MCP 서버 테스트
1. Go 서버 시작 (터미널 1)
터미널 1에서 다음 명령을 실행하여 (1부에서 구축한) Go 서버를 시작합니다. 이 서버는 gRPC 서비스와 REST 게이트웨이 역할을 모두 수행합니다.
2. MCP 서버 설정 및 시작 (터미널 2)
uv (Python 패키지 관리자)를 설치한 후, 환경을 설정하고 MCP 서버를 시작합니다:
# Create Python virtual environment
uv venv
source .venv/bin/activate
# Install MCP server dependencies
uv pip install fastmcp httpx --native-tls
# Start MCP Inspector
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector \
uv \
--directory ./generated/mcp \
run \
mcp_server.py
3. MCP 도구 목록 테스트
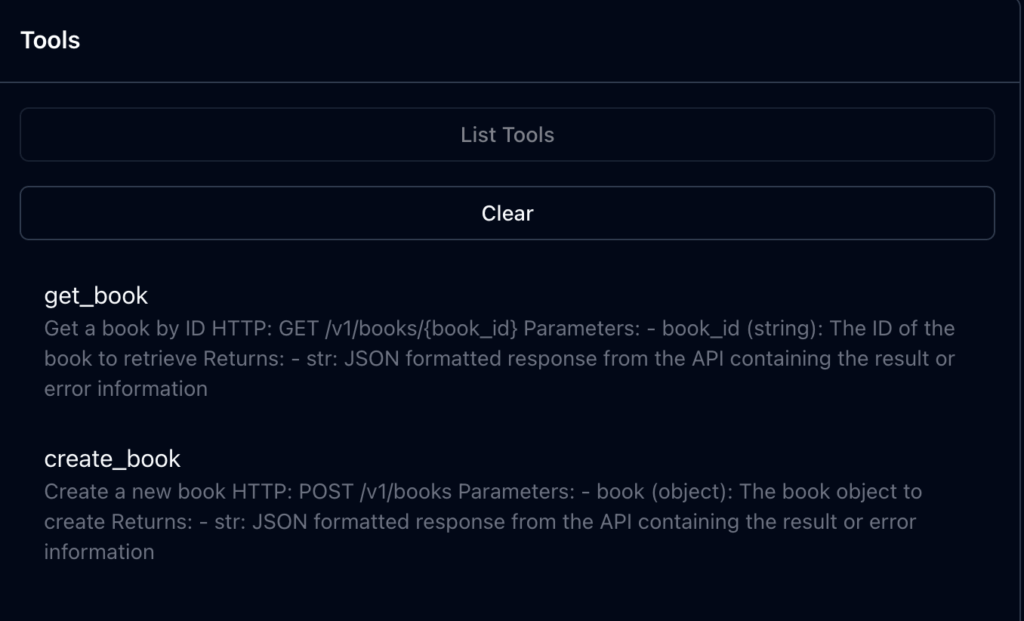
열린 MCP Inspector UI 페이지에서 연결한 다음 모든 도구를 나열하면, **get_book**과 create_book 두 가지 도구가 표시되어야 합니다.
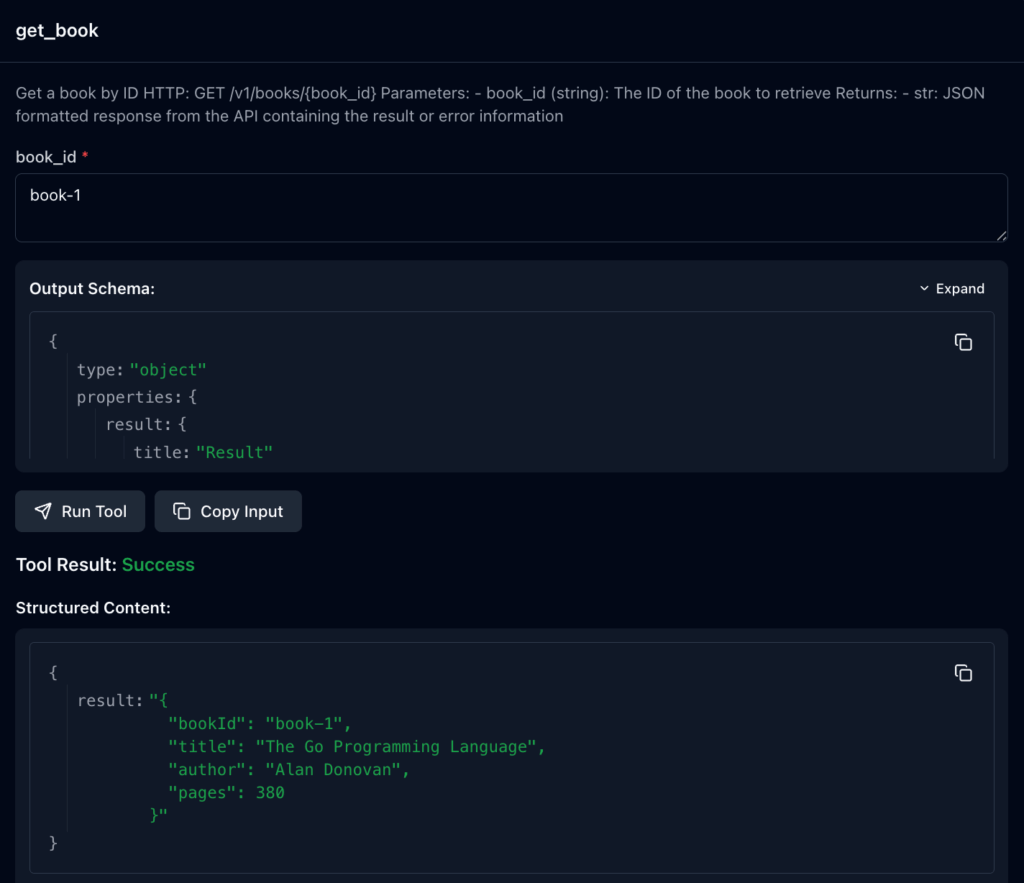
4. 도구 실행 테스트
get_book 도구를 선택하고, **book_id**에 **book-1**을 입력하고 실행합니다. 이는 **curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/v1/books/book-1**과 동일한 결과를 반환해야 합니다.
결론
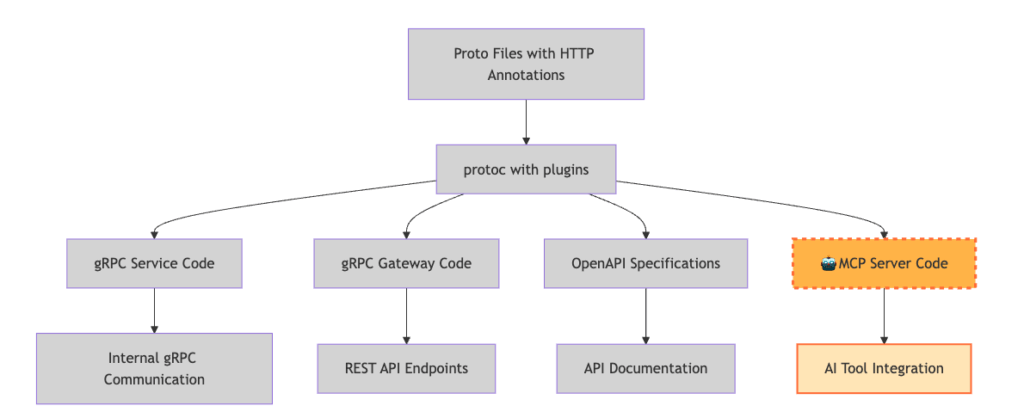
이제 하나의 proto 파일이 세 가지 다른 인터페이스를 생성하는 완전한 파이프라인을 갖게 되었습니다:
# Test gRPC interface
grpcurl -plaintext -d '{"book_id": "book-1"}' localhost:9090 bookstore.v1.BookstoreService/GetBook
# Test REST interface
curl http://localhost:8080/v1/books/book-1
# Test MCP interface (as shown above)
세 가지 모두 동일한 북 데이터를 반환해야 합니다!
동일한 proto 파일에 이제 gRPC 서비스, REST 엔드포인트, OpenAPI 사양 및 MCP 도구를 생성하는 데 필요한 모든 것이 포함되어 있습니다.
다음 단계
생성된 MCP 도구를 AI 에이전트로 테스트하기 시작했을 때, 작동하는 도구만으로는 충분하지 않다는 중요한 사실을 빠르게 깨달았습니다. AI 에이전트는 각 도구가 무엇을 하는지, 언제 적절하게 사용해야 하는지 이해하기 위해 풍부하고 상세한 설명이 필요합니다. 3부에서는 proto 주석이 AI 상호작용을 안내하는 지능적인 MCP 도구 문서가 되는 방법을 보여줄 것입니다.
메일: salesinquiry@enterprisedb.com

